IGCSE International Mathematics (0607)
Instructor
beyondcountables.com
37
Students
enrolled
- Description
- Curriculum

Course description
Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics motivates learners to improve their mathematical abilities, viewing them as essential life skills and a strong basis for further studies in mathematics or to support skills in other subjects. It enhances students’ proficiency, confidence, and skill in applying methods with or without the aid of a graphic display calculator.It cultivates learners’ abilities in mathematical inquiry and/or modeling, promoting both conceptual understanding and proficiency in applying techniques and methods.
Our Approach to Teaching and Learning:
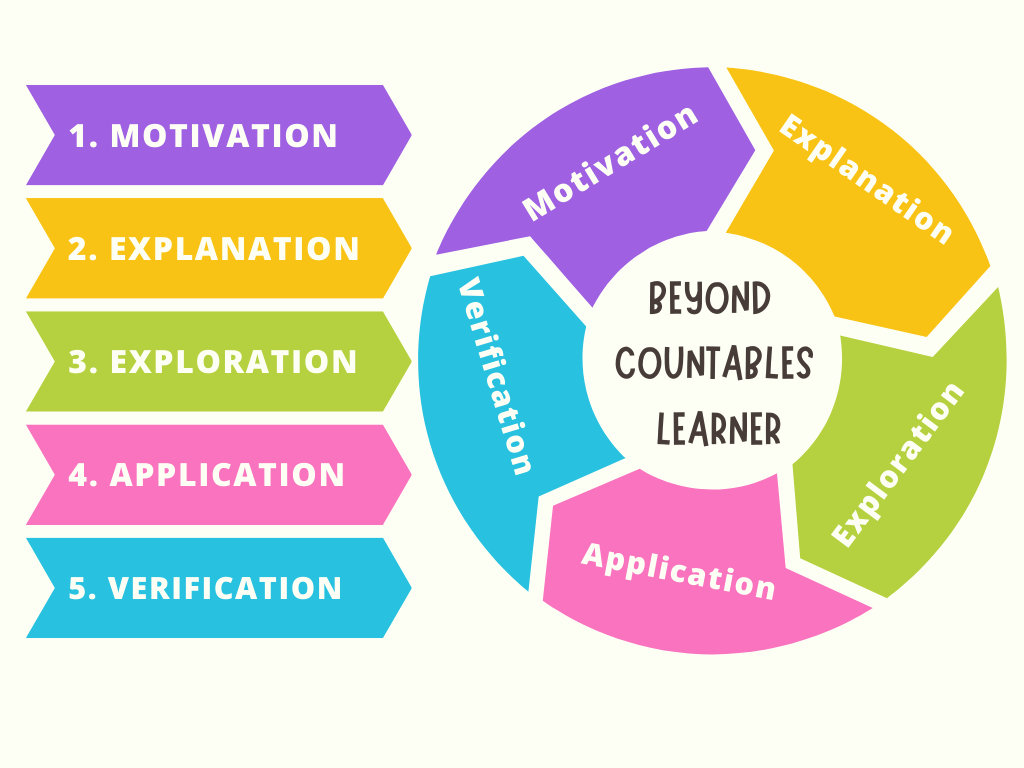
We follow the 5-step process depicted in the picture below.
Course syllabus
-
1Numbers
- Identifying types of numbers
- Set language
- Square roots and cubic roots
- Fractions, decimals and percentage
- Uses and rules of indices
- Conversion and calculation in standard form
- Degrees and Estimation
- Understanding ratios and proportion
- Rates
- Time and Money
- Exponential growth and decay (E)
- Surds (E)
-
2Algebra
- Simplification, expansion and factorization of algebraic expression
- Manipulation and factorization of algebraic fractions
- Simplify algebraic fractions.
- Indices and rules of Indices
- Solving simultaneous equations (using GDC)
- Represent and interpret inequalities
- Finding the nth term of the sequence
- Identifying variation model for the given data (E)
-
3Functions
- Identifying linear and quadratic function foe the given graphs
- Sketching the graph( using GDC)
- Usage of function notation
- Finding the quadratic equation (E)
- Asymptotes (E)
- Transforming graphs (E)
- Usage of logarithmic functions (E)
-
4Coordinate geometry
- Cartesian coordinates in two dimensions
- Gradients
- Finding the midpoint
- Equation of straight line
- Gradient and equation of parallel lines
- Gradient and equation of perpendicular lines (E)
-
5Geometry
- Usage of geometrical terms
- Construction of lines and angles
- Three figure bearing
- Similarity and symmetry
- Properties of angles
- Circle theorem
- Symmetry properties of circle (circle theorem II)
-
6Mensuration
- Metric units of measurements
- Calculating area and perimeter
- Circles, arcs and sectors
- Surface area and volume of three dimensional shapes
- Compound shapes and solids
-
7Trigonometry
- Understanding pythagoras theorem
- Right angled triangle and their ratios
- Trigonometric functions and their values (E)
- Sine rule and cosine rule (E)
- Trigonometry in 3D (E)
-
8Transformations and vectors
- Types of transformation
- Operations in vectors (E)
- Finding magnitude in vector (E)
-
9Probability
- Introduction to probability
- Estimating relative and estimated frequency
- Probability of two events
-
10Statistics
- Tabulation and interpretation of statistical data
- Difference between discrete and continuous data.
- Mean, median, mode and range (using GDC)
- Statistical charts and diagram
- Scatter diagram
- Cumulative frequency and histogram (E)