IBDP Mathematics: Application and Interpretation (AISL)
Instructor
beyondcountables.com
36
Students
enrolled
- Description
- Curriculum
Our Approach to Teaching and Learning:
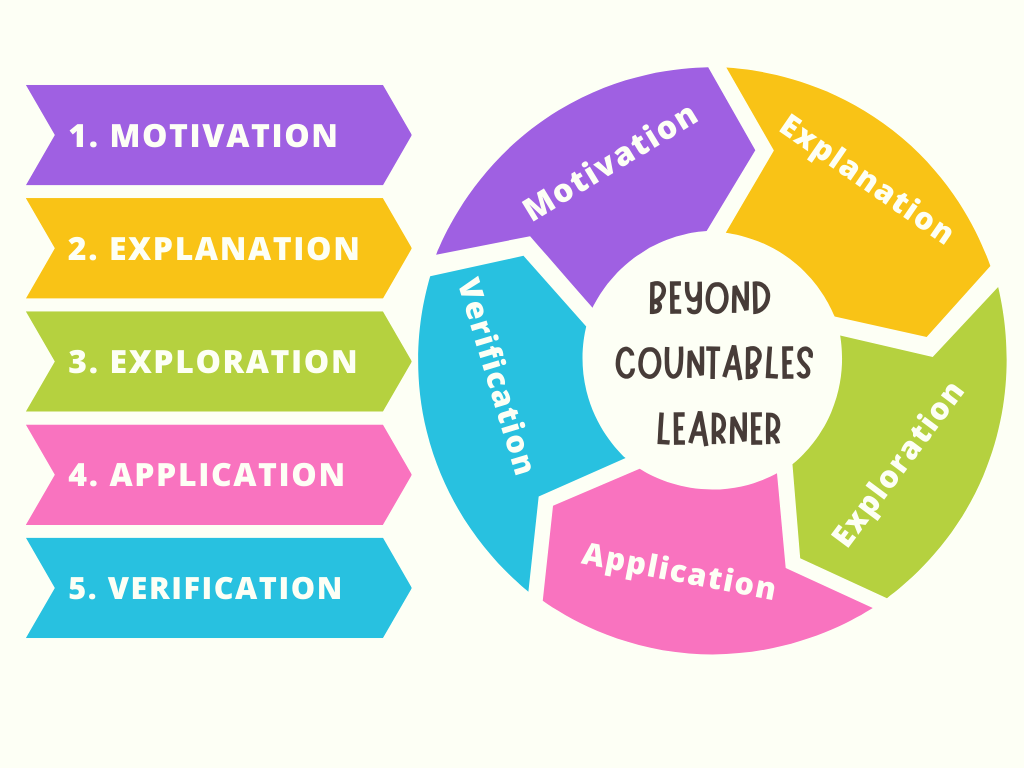
We follow the 5-step process depicted in the picture below.
AISL course content is covered under five topics.
-
1Number and Algebra
- Arithmetic and geometric sequence and series
- Applications of arithmetic and geometric sequence and series
- Logarithms
- Errors and estimation
- Amortization and annuities using technology
- System of equations and polynomials using technology
-
2Functions
- Equation of straight lines, parallel and perpendicular lines
- Function definition and notation
- Domain and Range of functions
- Inverse and composition function
- Sketching graphs of functions and determining its key features
- Mathematical modelling - Modelling Linear, Quadratic, cubic, exponential, and sinusiodal functions
-
3Geometry and trigonometry
- 3D mensuration
- Sine rule, cosine rule and area of a triangle (non-right angled)
- Angle of elevation and depression and its applications
- Circular Measure - Radians, length of arc and area of sector
- Voronoi diagrams
-
4Statistics and probability
- Sampling techniques
- Data types and their representations - Cumulative frequency & Box and whisker diagrams
- Measures of central tendency - Mean, Median and Mode
- Measures of spread - Range, Variance/Standard deviation and IQR
- Linear correlation - Bivariate Analysis
- Scatter diagrams
- Pearson Correlation coefficient
- Line of best fit and regression line
- Essentials in Probability
- Probability calculations in Venn diagrams, Tree diagrams and Two way tables
- Conditional Probability
- Discrete Random Variable and its Expectation/ Mean and Variance
- Binomial Distribution
- Continuous Random Variable and its Mean, Median and Variance
- Normal Distribution
- Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient
- Hypothesis testing
-
5Calculus
- Concept of limit
- Derivative as a gradient function or as a rate of change
- Derivatives from First principles
- Increasing and Decreasing behavior of functions
- Equation of tangents and normals
- Integration as Ant-differentiation - Indefinite integrals
- Integration as Area under curve - Definite integrals
- Approximating areas using the trapezoidal rule